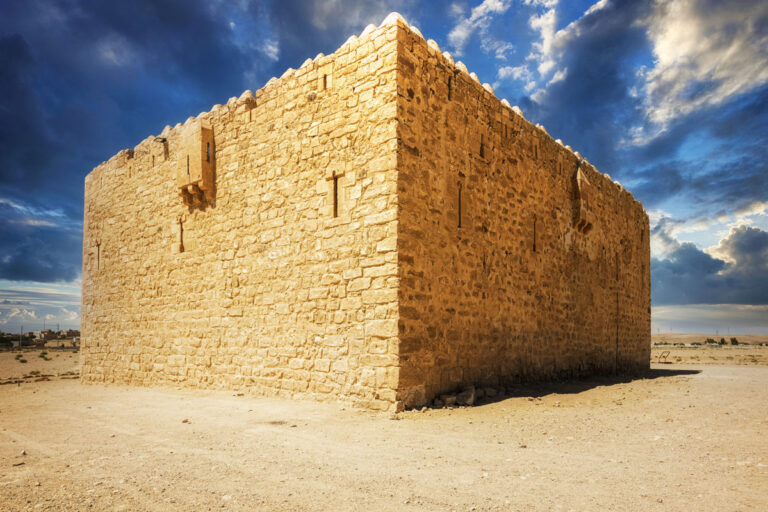
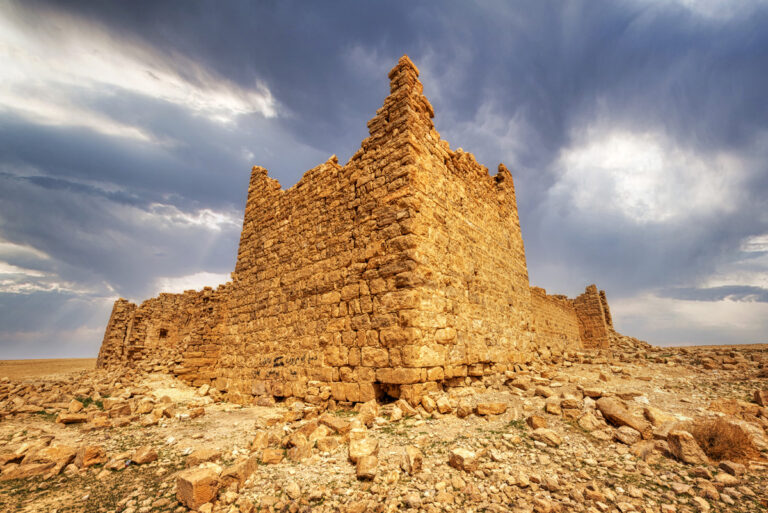
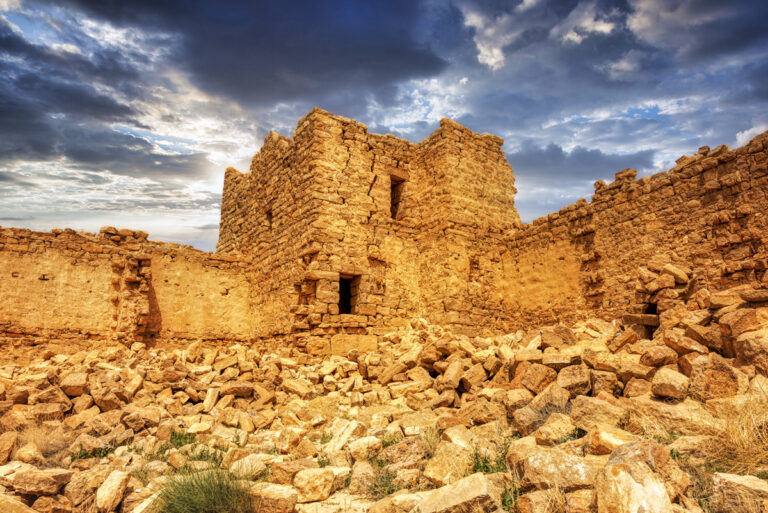
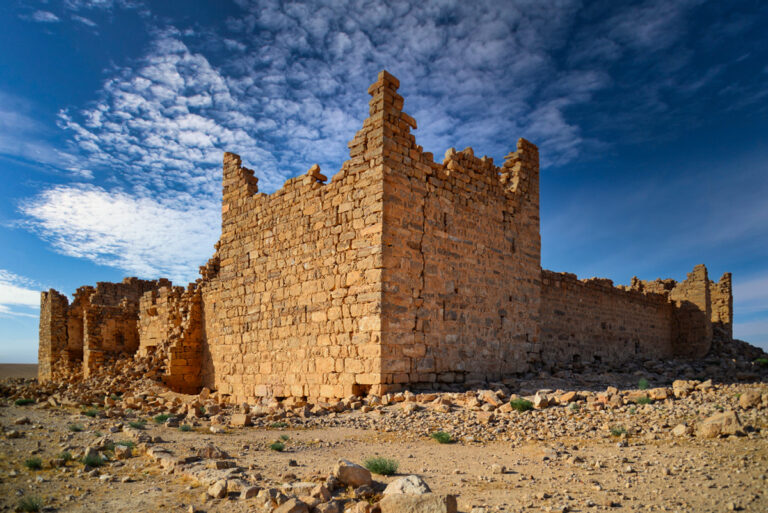
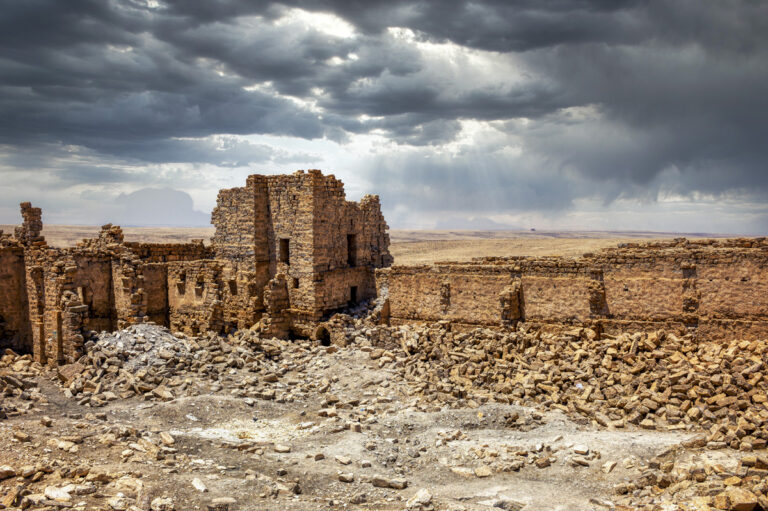
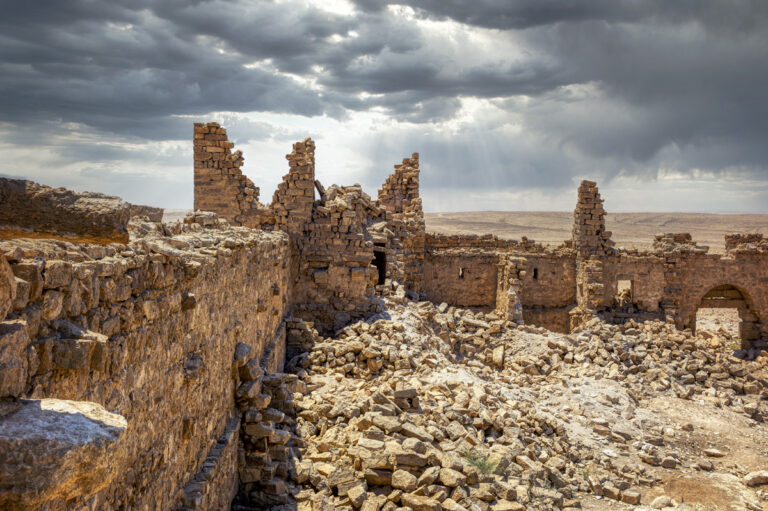
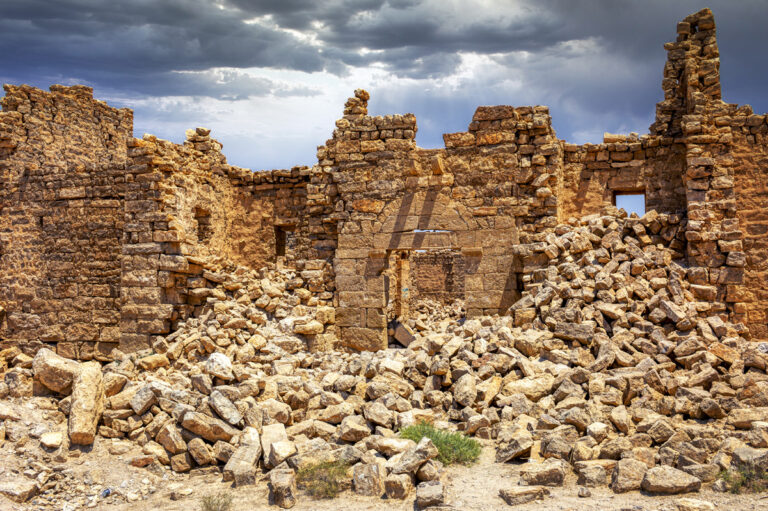
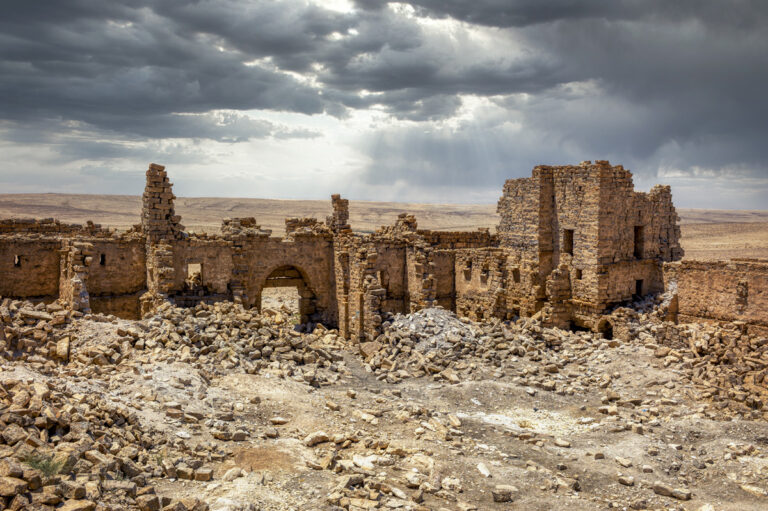
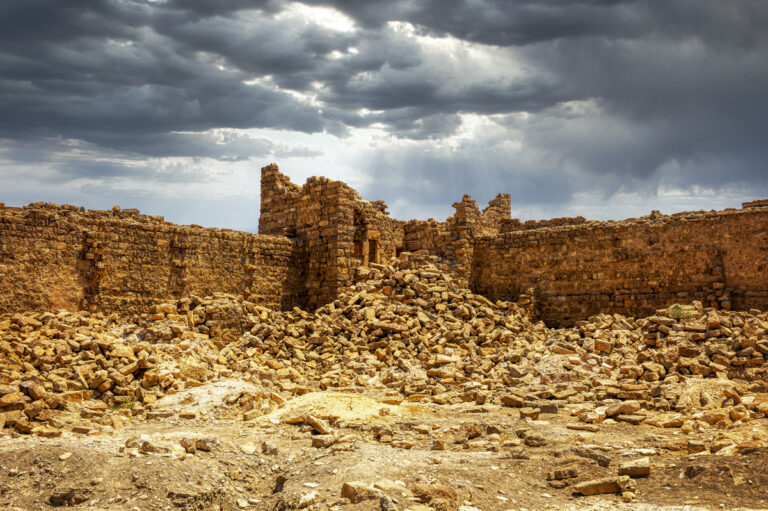
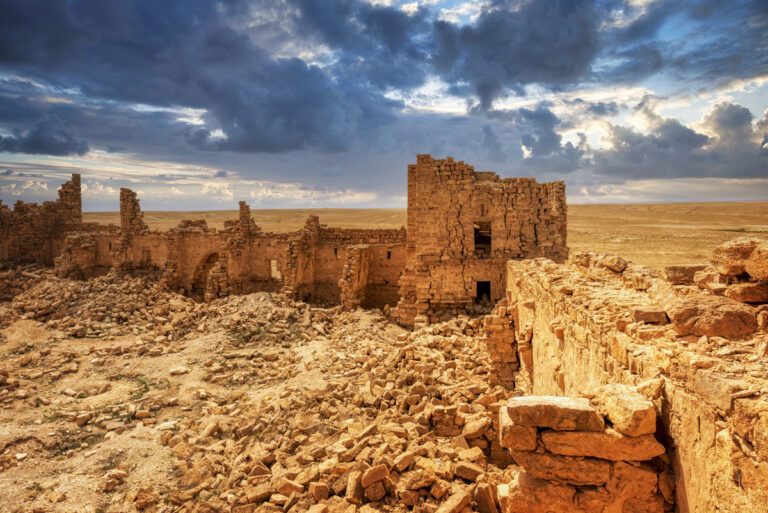
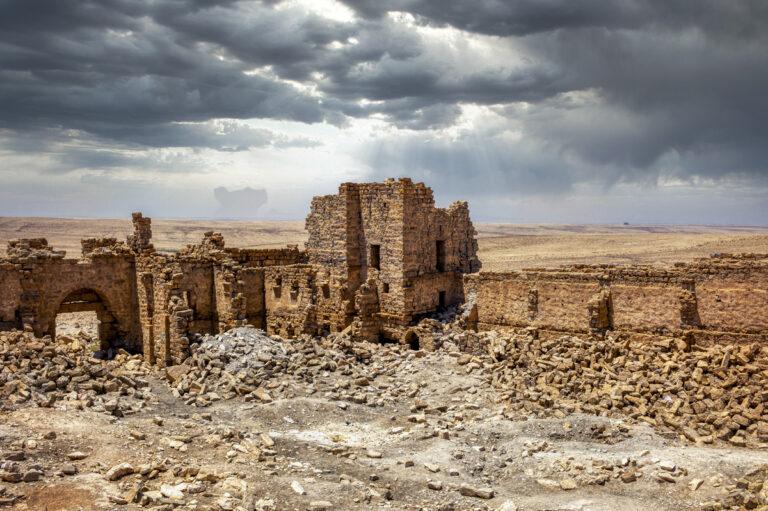
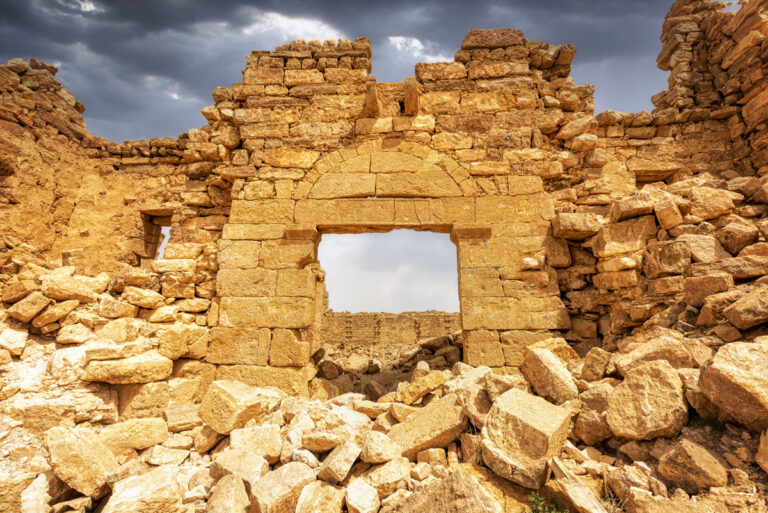
Qasr Bshir, also known as Castra Praetorii Mobeni, is a remarkably well-preserved Roman fort positioned in the heart of the Middle East. A vital part of the Limes Arabicus—a defensive network of forts and watchtowers—it was constructed to shield the province of Arabia from the swift incursions of desert nomads. Though not particularly violent, these nomads, with their dromedaries, could swiftly pillage vast tracts of countryside if provoked. According to a Latin inscription above the fort’s main gate, the structure was built between 293 and 305 CE during the reign of Emperor Diocletian.

A Strategic Location
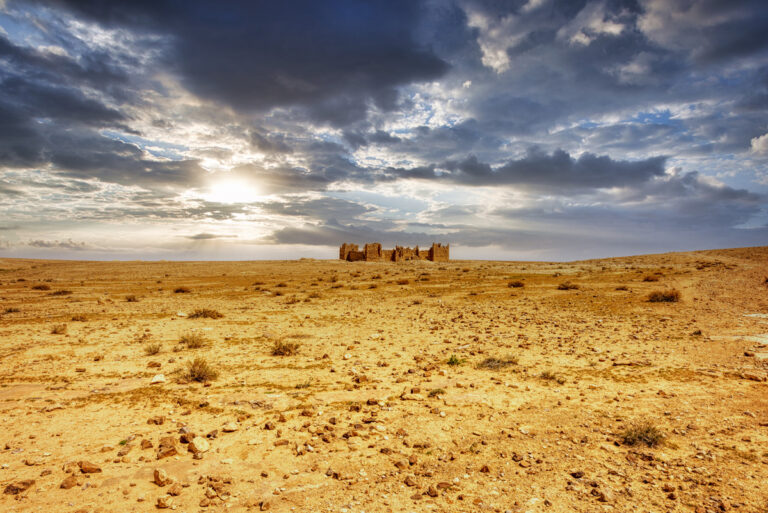
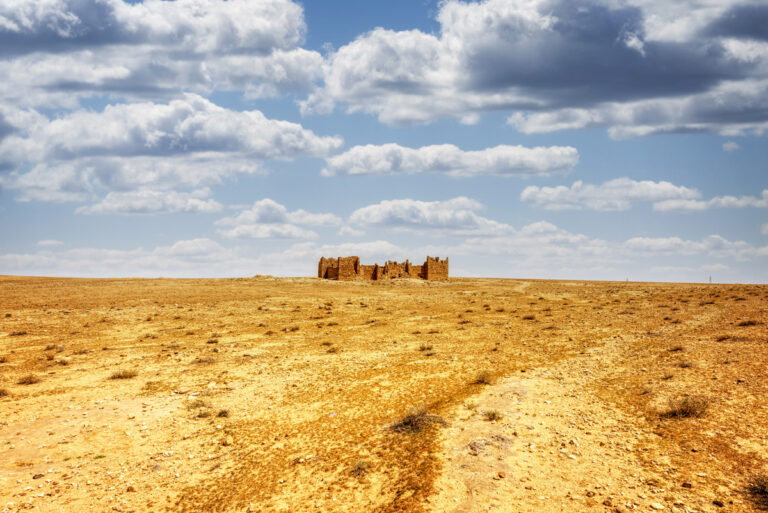
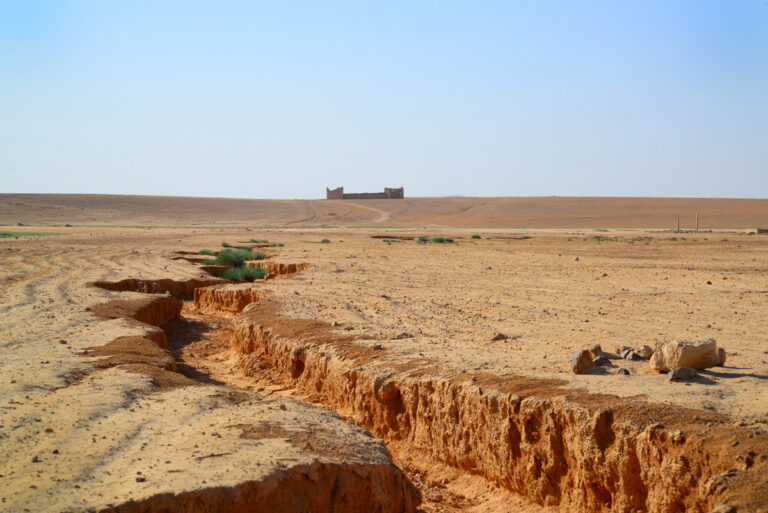
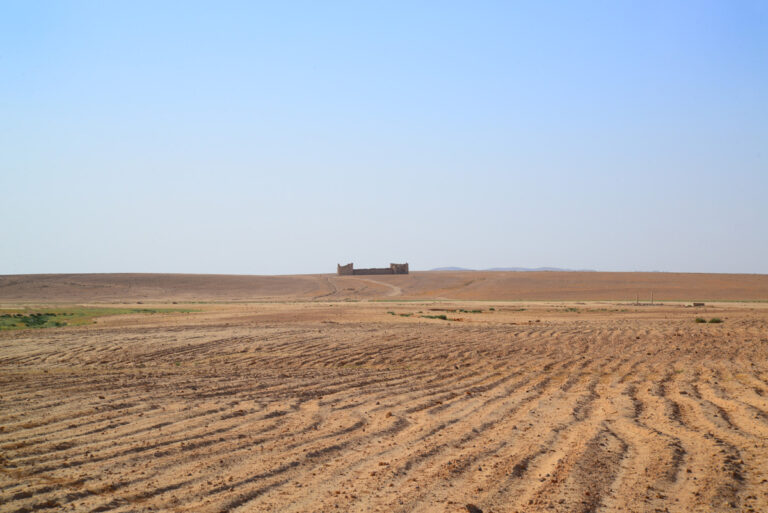
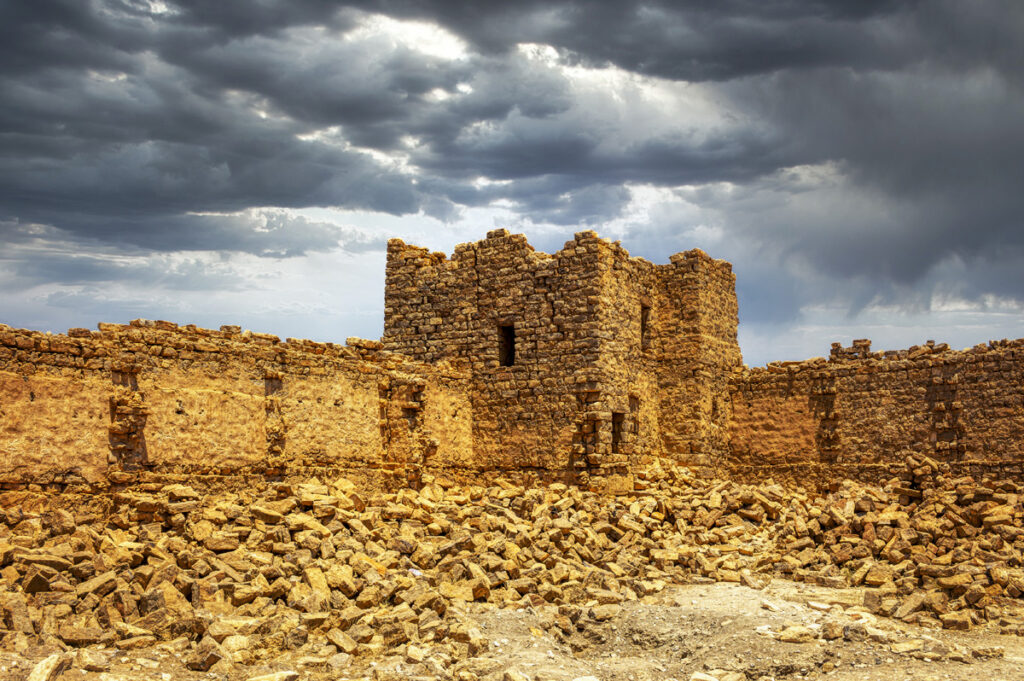
Set upon a windswept, stony plain intersected by a network of wadis that flow into Wadi Mujib and eventually into the Dead Sea, Qasr Bshir’s strategic location is immediately apparent. While the arid terrain appears daunting, agriculture along the fertile wadis has been practised for centuries. Visitors approaching the fort from the nearby road will cross cultivated fields in shallow valleys before being greeted by the imposing structure that looms above the landscape, commanding an uninterrupted view of its surroundings.
Architectural Grandeur
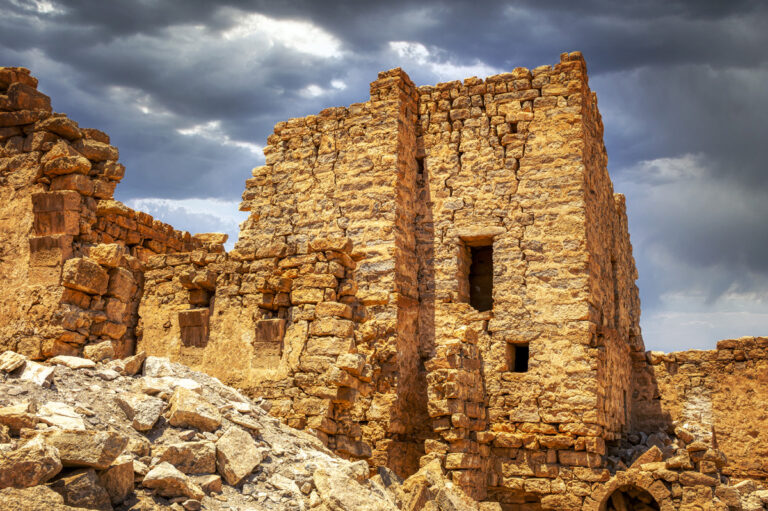
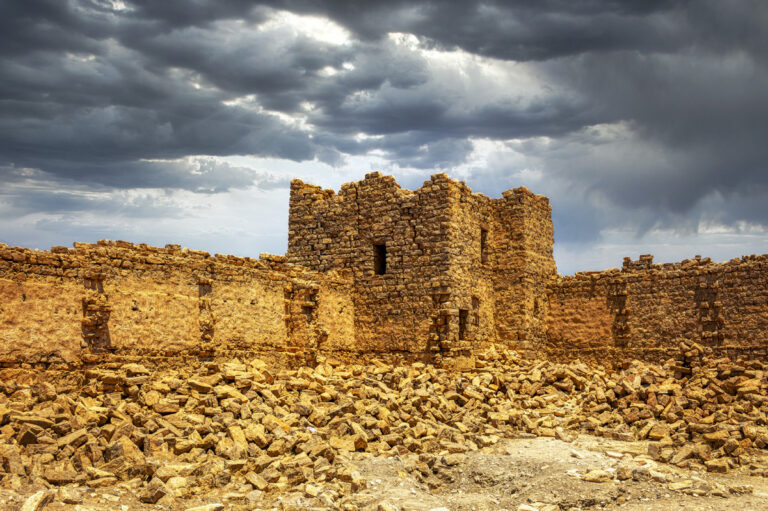
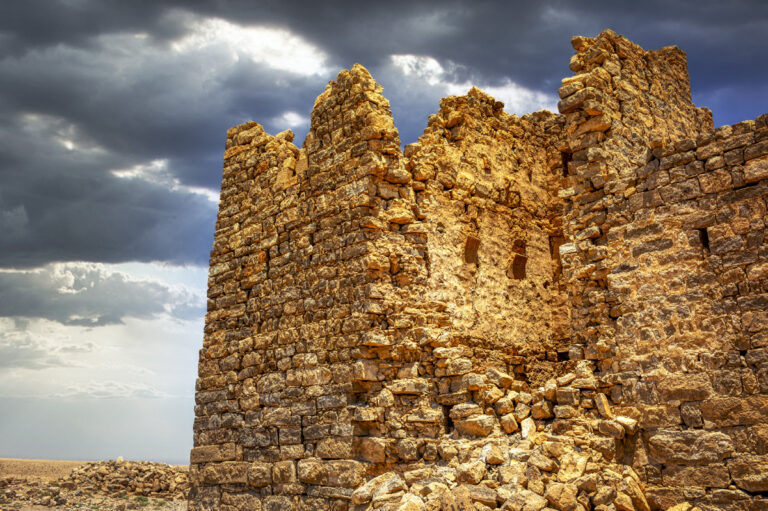
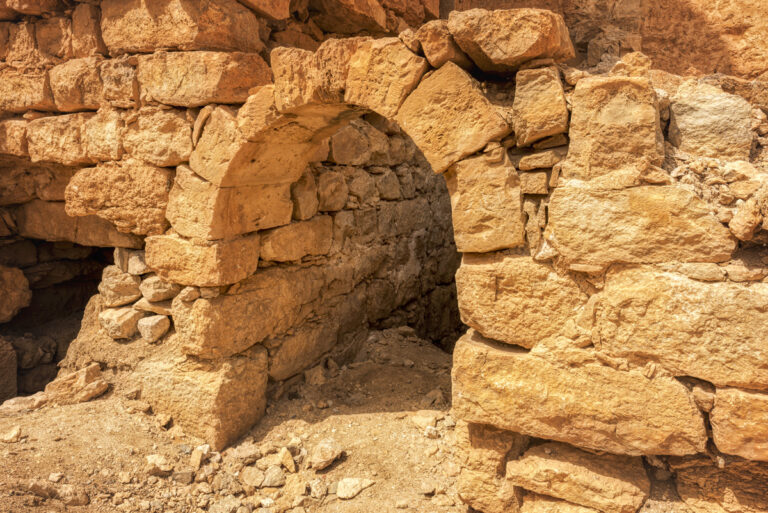
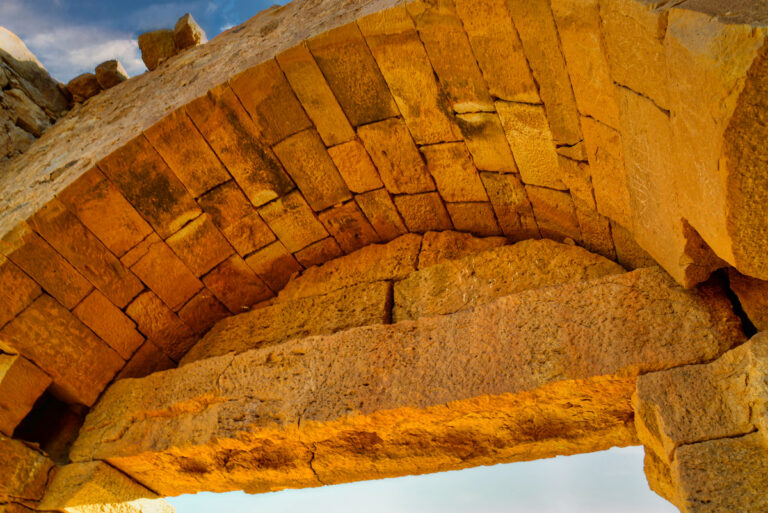
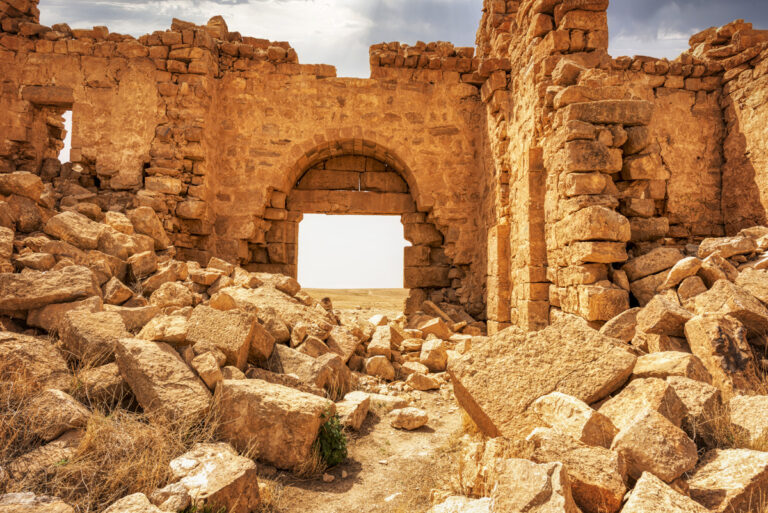
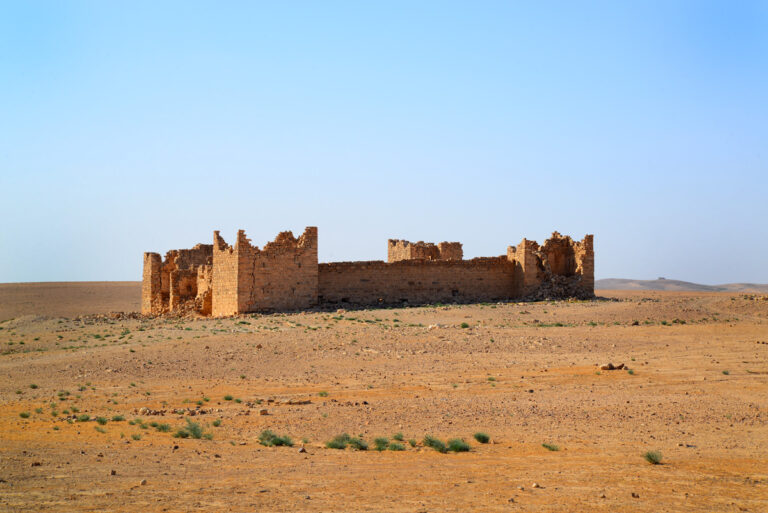
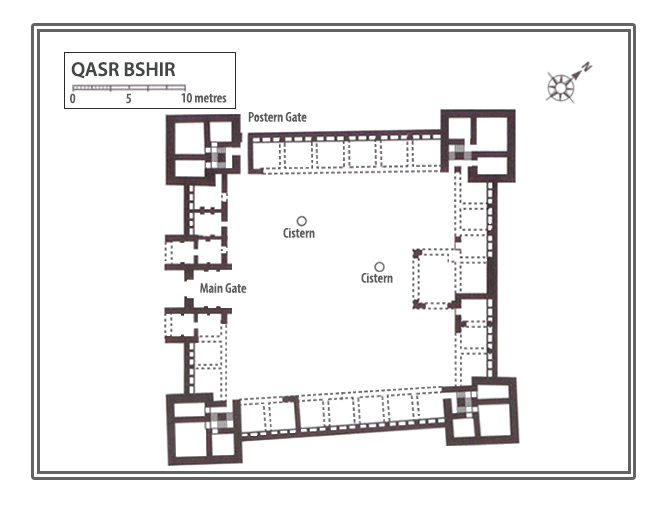
The fort itself is compact and commanding, spanning an area of approximately 57 by 54 metres. Its curtain walls, an impressive 1.5 metres thick and six metres high (without the rampart), remain in near-perfect condition, connecting four sturdy, square corner towers. Each tower measures around 11 to 12 metres, projecting three metres beyond the walls. These three-storied towers once stood over 10 metres tall, forming an intimidating defence line. On the western side, a discreet postern gate—less than a metre wide—provided a minor entry point.
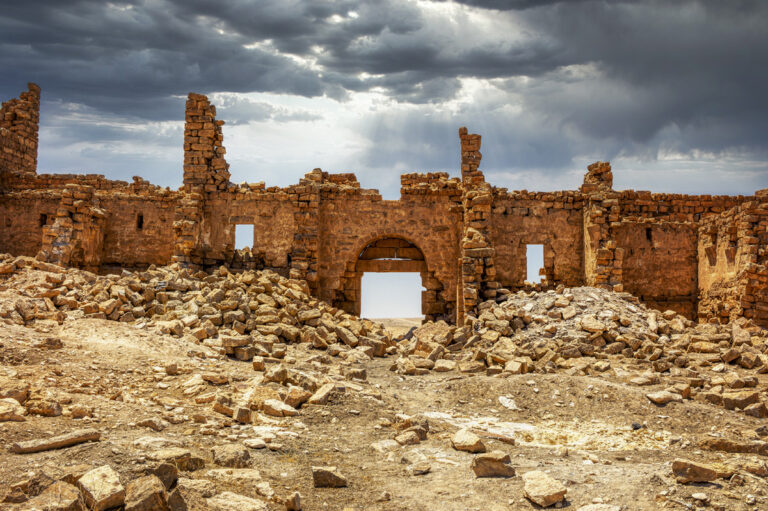
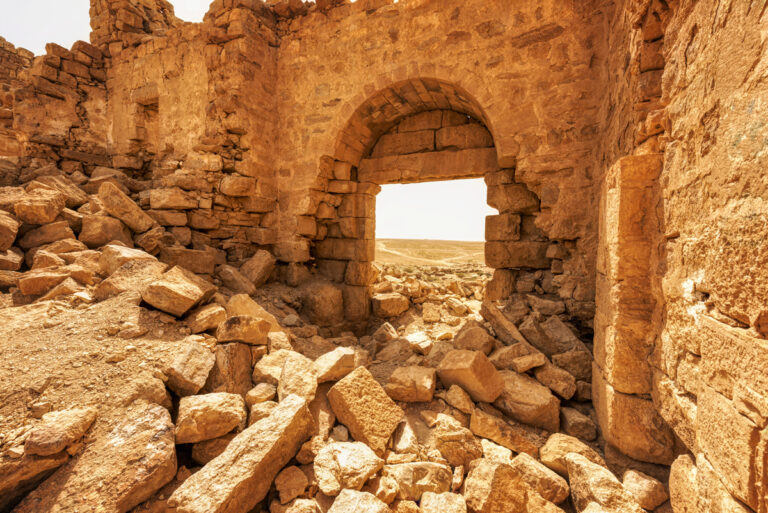
The main gate, located along the southwestern aspect and facing the shallow valley, is flanked by two smaller towers, roughly half the size of the corner ones. These sentinel-like structures, together with the central gate, gave the impression of both authority and protection.
Interior Features and Functionality
Inside the walls, the courtyard reveals a practical yet efficient layout designed for Roman military needs. Surrounded by 23 rooms identified as stables, the ground floor served as a functional space for housing horses and supplies.
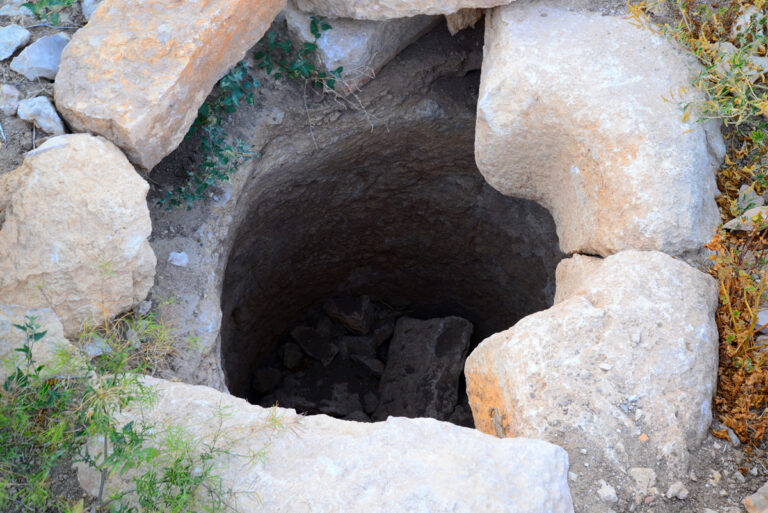
Large enough to accommodate the daily operations of a military outpost, the courtyard also features two cisterns that collected and stored rainwater, a vital resource in this arid region.
Above the stables, a second story provided living quarters for soldiers. The flat roof of these barracks extended to the height of the rampart, creating an extensive and seamless fighting platform. The design ensured that those defending the fort could move efficiently while maintaining a commanding view of their surroundings.
Layers of History
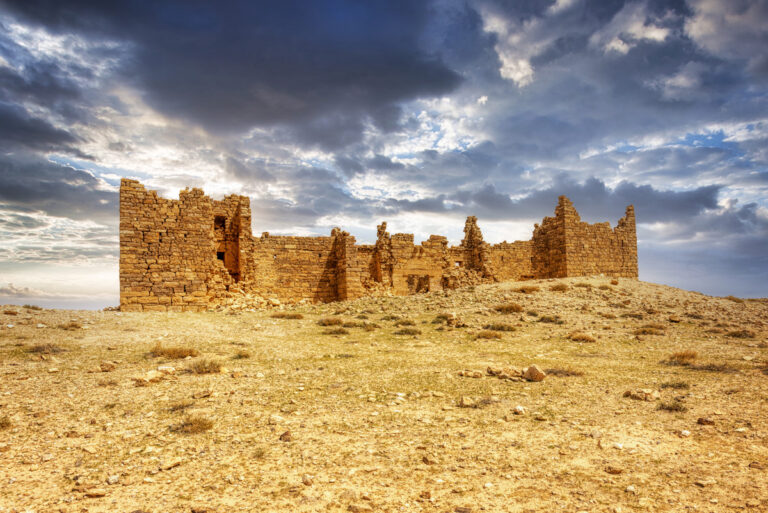
The site on which Qasr Bshir stands has long been recognised for its strategic value. Before the Romans erected their fort, the location had been guarded by a Nabataean stronghold, remnants of which lie beneath the current structure. Additionally, nearby stand two Iron Age towers—Qasr el-Al and Qasr Abu el-Kharaq—further evidence of the area’s historical importance. Both towers were later reused by Nabataean and Roman forces. It is likely that an ancient road, possibly connecting the nearby Roman legionary base at Lejjun, ran close by, further emphasising the site’s military and logistical significance.
Visiting Qasr Bshir
For modern visitors, this historic marvel is accessible from Jordan’s Desert Highway. Travelling from Amman, you will turn right after the Qatrana Manaseer gas station and continue for approximately 10.5 kilometres before taking a less conspicuous right turn. The final leg of the journey requires either a 4×4 or crossover vehicle to tackle the rugged terrain, though alternatively, a two-kilometre walk from the parking area leads directly to the fort. The effort rewards you with not just a close encounter with Qasr Bshir’s magnificence but also sweeping views of the surrounding windswept plains and cultivated wadis.
Immerse Yourself in History
Qasr Bshir is more than just a Roman relic; it is a testament to the ingenuity, foresight, and endurance of those who built and occupied it. Whether you’re marvelling at the precision of its walls, imagining the bustling life within its barracks, or exploring the nearby ancient towers, this site offers an unforgettable glimpse into centuries of strategic military history.

Key Moments in History
Construction during Diocletian's Era (293–305 AD)
Built under the reign of Emperor Diocletian, Qasr Bshir served as a strategic fortification in the Roman Limes Arabicus to secure the empire's southeastern borders.
A Roman Military Outpost
Functioning as a key military station, it housed Roman soldiers who monitored the desert surroundings and ensured protection from potential threats.
Key Moments in History
Construction during Diocletian's Era (293–305 AD)
Built under the reign of Emperor Diocletian, Qasr Bshir served as a strategic fortification in the Roman Limes Arabicus to secure the empire's southeastern borders.
A Roman Military Outpost
Functioning as a key military station, it housed Roman soldiers who monitored the desert surroundings and ensured protection from potential threats.
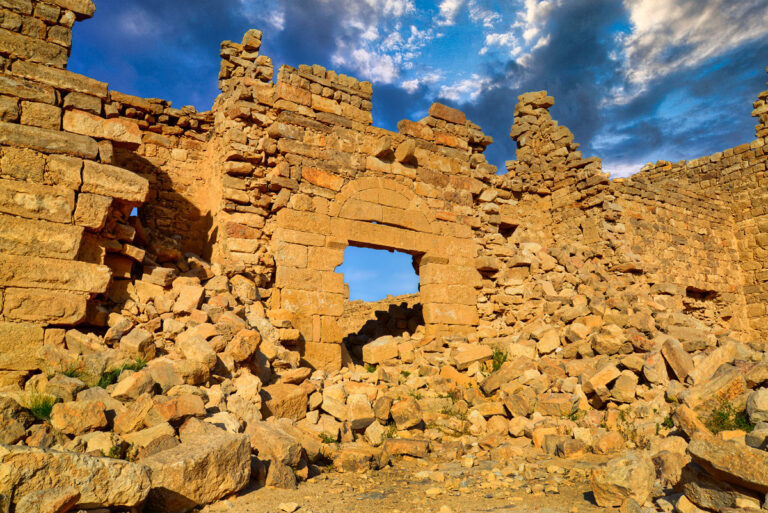
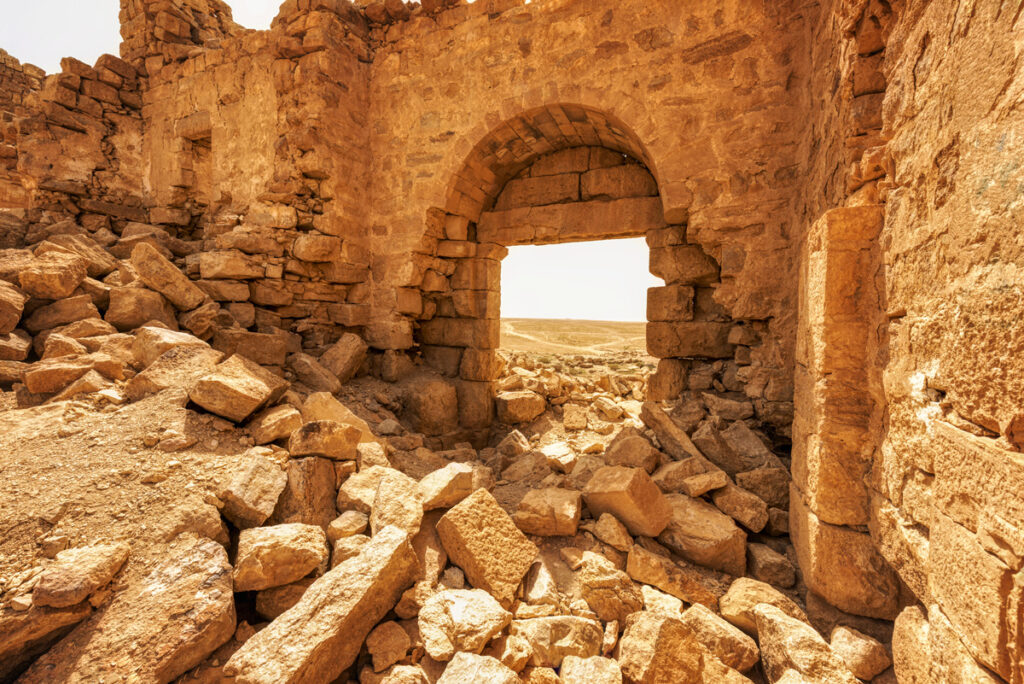
Latin Dedication Inscription
The main gate features a rare Latin inscription, celebrating its establishment and linking it to the legacy of Roman engineering and governance.
Modern Recognition and Preservation
Now preserved as a well-maintained historical site, Qasr Bshir continues to capture interest for its architectural brilliance and cultural significance in Jordan and beyond.