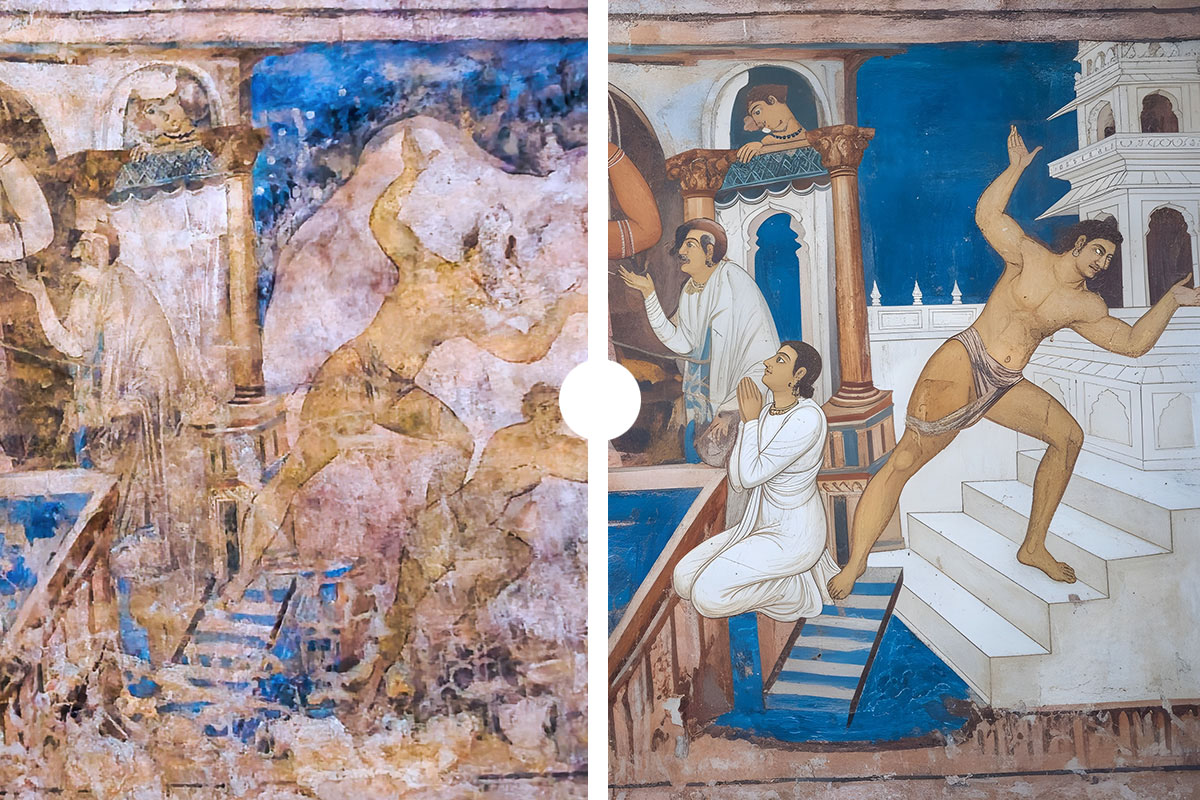
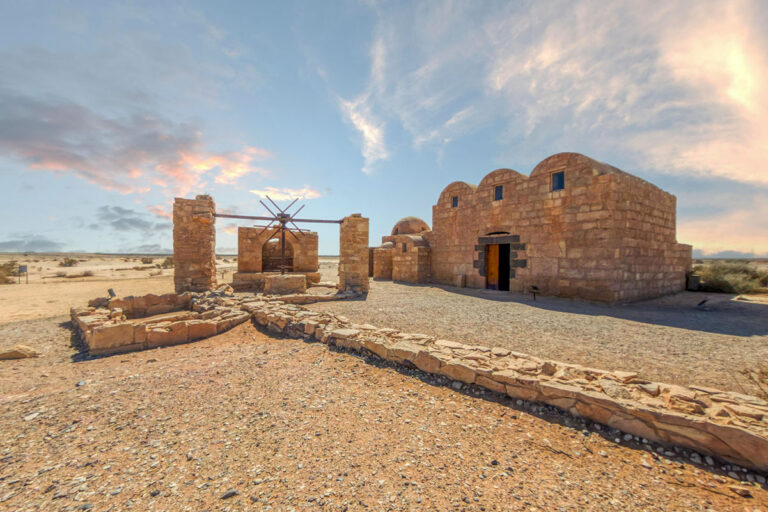
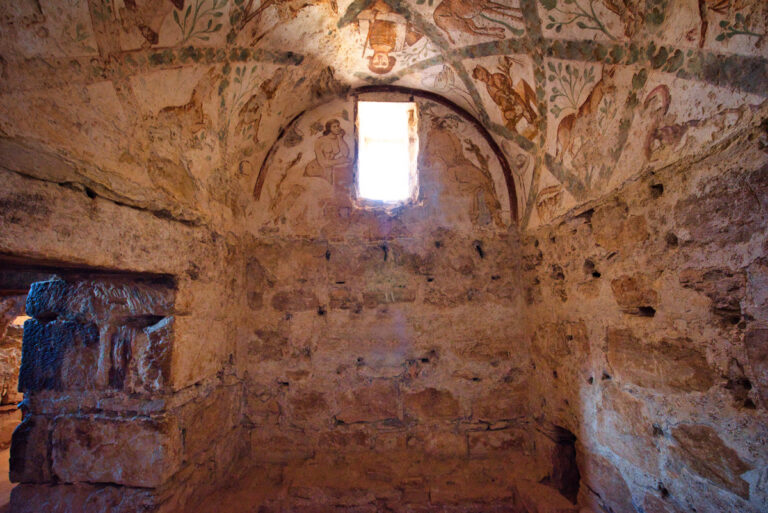
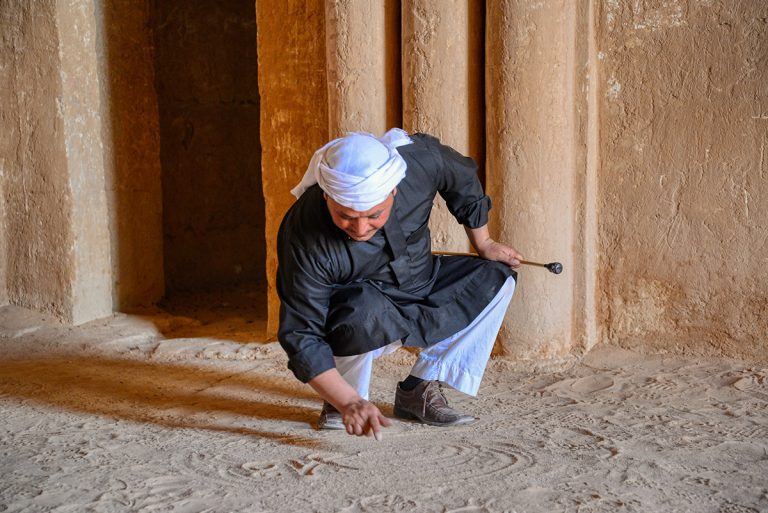
The frescoes of Qasr Amra, a UNESCO World Heritage site in Jordan, are among the most remarkable artistic legacies of the early Islamic world. Painted in the early 8th century, they depict celestial constellations, hunting scenes, musicians, rulers, and mythological figures. Yet after more than a thousand years of exposure, many of these vivid paintings have faded, cracked, or vanished altogether. Today, artificial intelligence is opening new possibilities for their revival—without ever touching the fragile originals.
The Process of AI Restoration
The journey begins with high-resolution and multispectral photography, capturing every visible and invisible trace of pigment. These images are processed by AI algorithms trained to separate original paint from damage caused by erosion, soot, and previous restorations. Once the authentic lines and colours are isolated, machine learning models analyse comparable frescoes, historical pigments, and Greco-Roman iconography to reconstruct missing or unclear details.
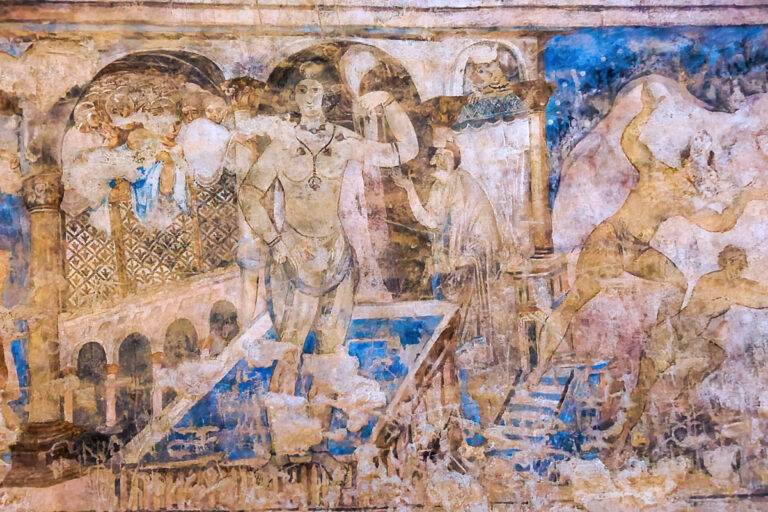
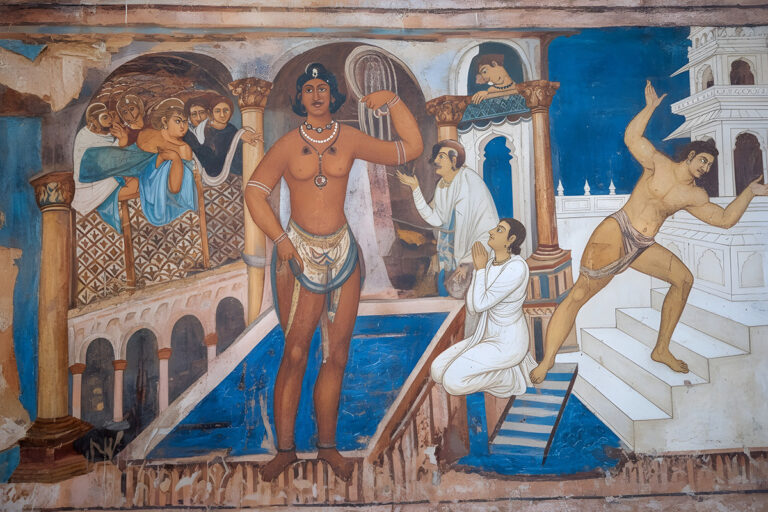


AI also helps predict the original colour palette, based on chemical pigment analysis and patterns across surviving sections. Finally, the digitally restored images are mapped onto 3D models of Qasr Amra’s interiors, allowing scholars and the public to virtually step into the bathhouse as it might have looked in its prime.
The Significance of Digital Revival
AI-assisted restoration carries profound cultural and scholarly significance. It provides a non-invasive preservation method, ensuring the frescoes remain untouched while still revealing their lost beauty. For historians and archaeologists, these reconstructions shed light on themes central to the Umayyad court: the blending of Greco-Roman, Persian, and Arab traditions, and the ruler’s role as a worldly and cosmic authority.
Beyond scholarship, the restored frescoes have educational and experiential value, allowing visitors worldwide to engage with Umayyad art in ways previously impossible. As the frescoes continue to deteriorate, their digital revival serves as a cultural safeguard, preserving a visual record for generations to come.
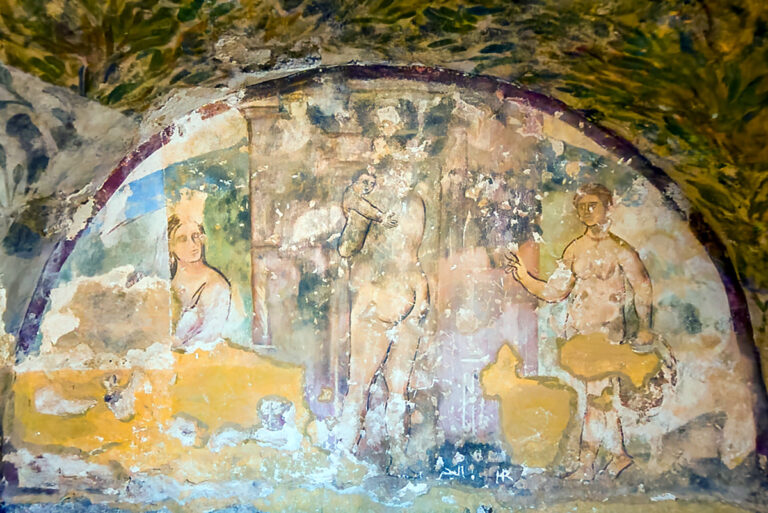
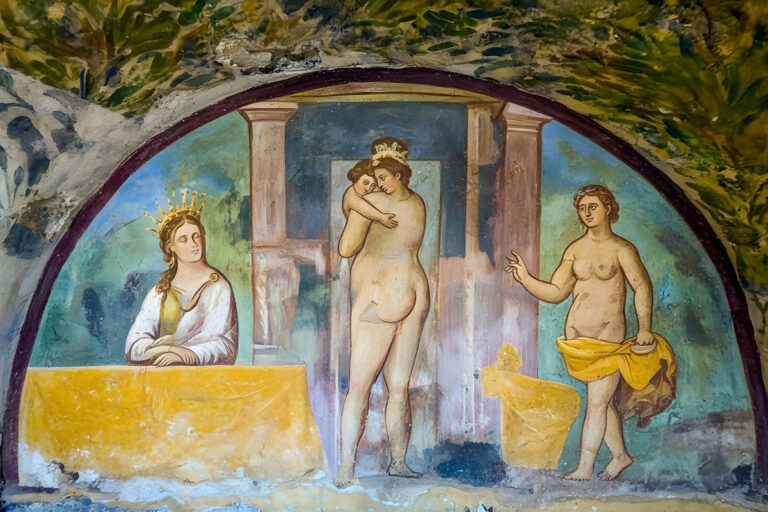


How Accurate Are AI Restorations?
AI excels at pattern recognition. By analysing surviving fragments of a fresco and comparing them with databases of contemporary Byzantine, Roman, and Umayyad artworks, AI can generate plausible reconstructions. Advanced algorithms also estimate the original pigments, drawing on chemical analyses of paint residues and knowledge of ancient color palettes. The result is a visually coherent image that aligns with the artistic style of the early 8th century.
While these reconstructions can be remarkably convincing, they remain interpretive models rather than definitive restorations. AI is strongest when filling small gaps or faded details, but less reliable when entire sections of a fresco are missing.
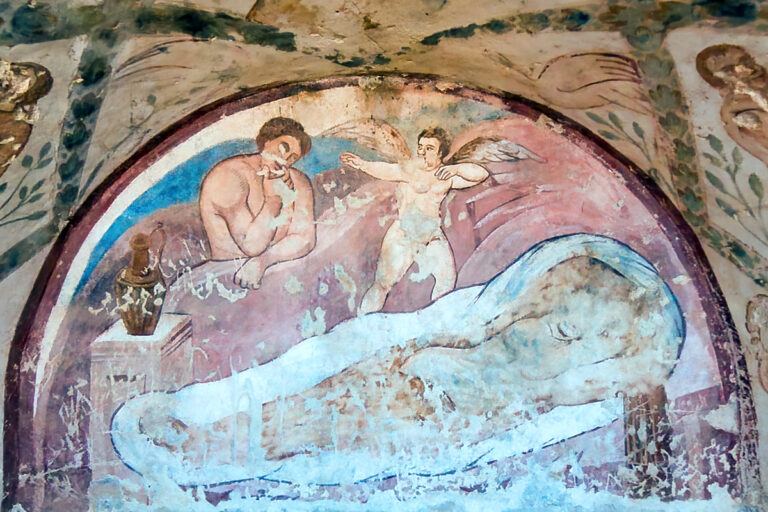
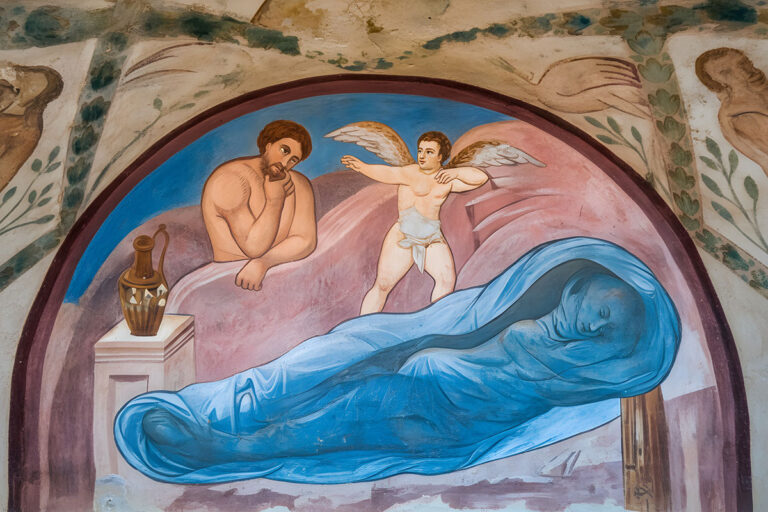


Limitations of the Technology
Despite its promise, AI has clear limitations. Large-scale gaps often lead to speculative results, where the program generates “best guesses” that may not reflect historical reality. Training data can also introduce bias—for example, overemphasising Byzantine stylistic features at the expense of local Umayyad nuances.
Another limitation is the loss of subtlety. Fine brushwork, symbolic gestures, or regional details may not be fully captured. For this reason, scholars stress that AI-generated images should be seen as visual aids, not as replacements for the originals.
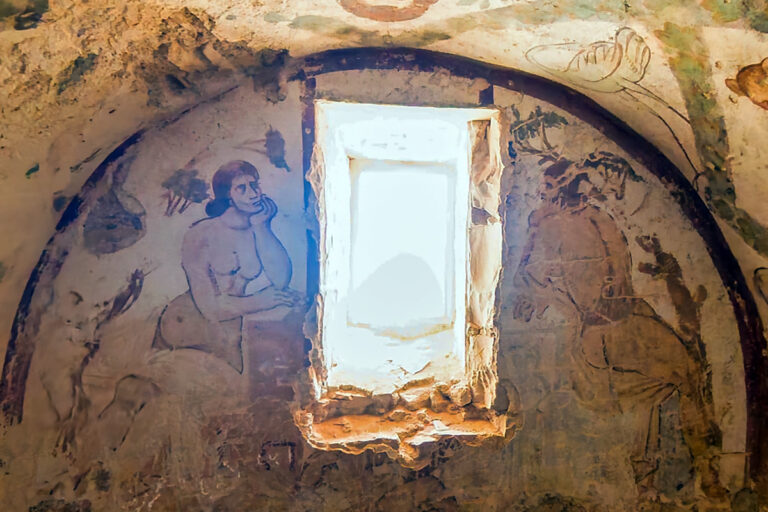
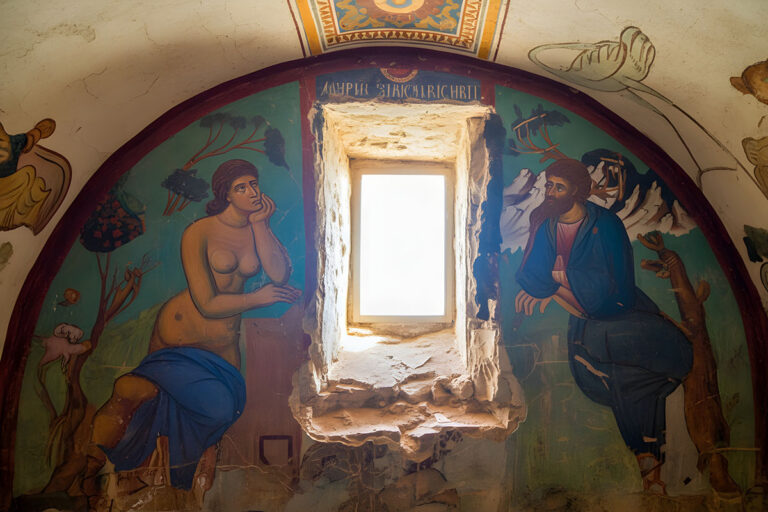


Future Possibilities
The future of AI in cultural heritage looks promising. By combining AI with multispectral imaging, 3D scanning, and pigment analysis, restorations will become increasingly precise. Interactive reconstructions may allow museum visitors to switch between the fresco’s current state, its scholarly interpretation, and AI-enhanced visuals—making the process transparent.
Even more exciting is the possibility of predictive modelling, where AI simulates how frescoes looked in different historical periods, showing their gradual fading and restoration attempts. This could help both researchers and the public understand not only the art itself, but also the story of its survival.
For more information about Qasr Amra, you can visit the following links:
Qasr Amra Travel Guide
Frescoes of Qasr Amra Photo Album